Black Caiman
(Melanosuchus niger)

Rio Negro-Juru Moist Forests
STATISTICS
Length up to
6 meters
Weight up to
40 kgs
Lifespan
80 years
Skilled Hunter - Acute Eyesight - Excellent Hearing - Immense Biting Strength
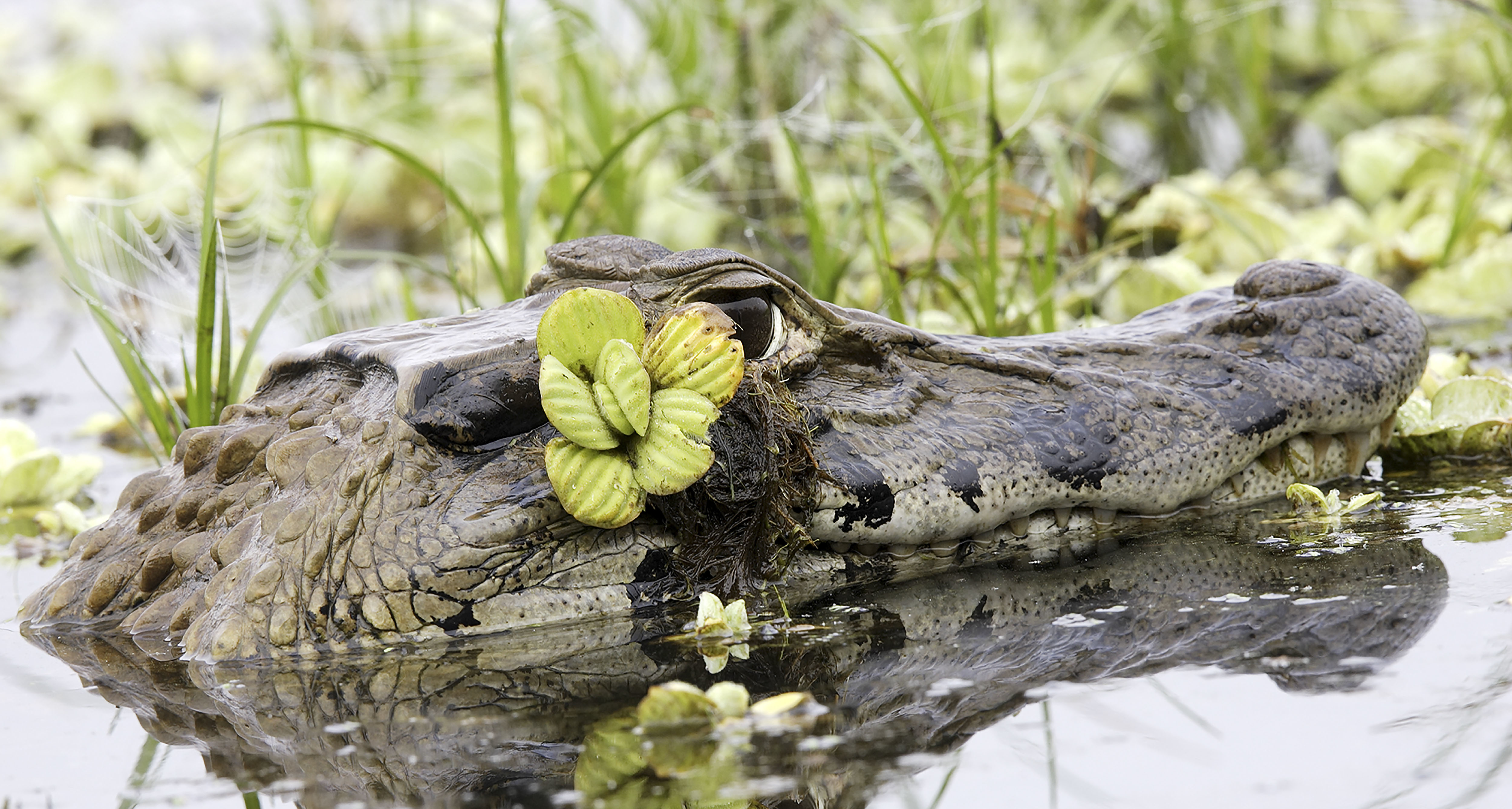
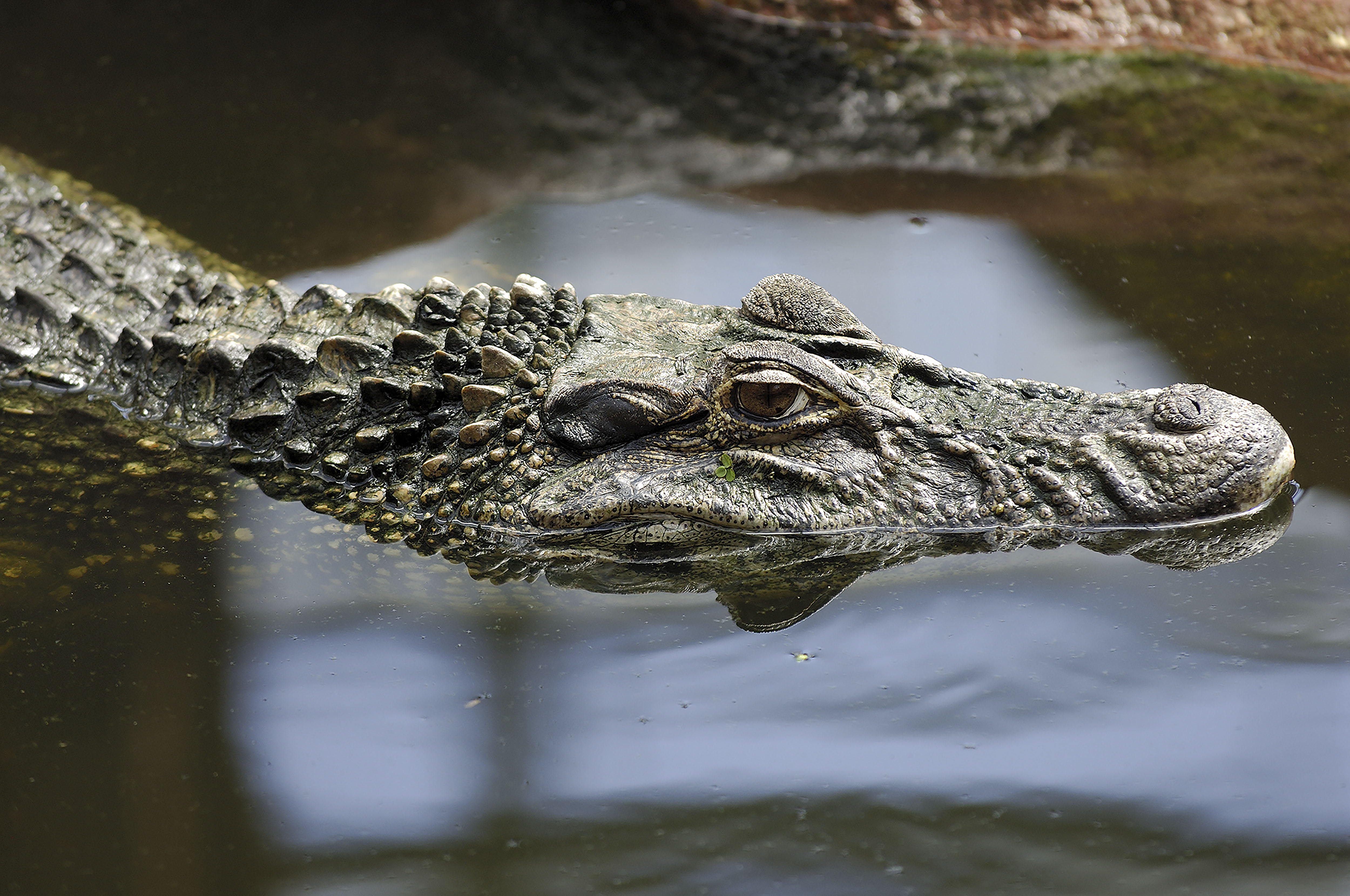
The Black Caiman is the largest of the alligator species that reside in shallow, freshwater habitats, venturing into flooded savannah and wetlands. The Black Caiman’s dark, protective skin helps camouflage it at night and allows it to absorb heat. Its lighter underbelly is characterized by black markings. It has a broad snout that narrows towards the end.
An important keystone species and impressive aquatic hunter, the Black Caiman helps with nutrient cycling and preys selectively on certain fish species, specifically piranas, catfish, and mollusks. It has also been known to emerge out of the water and hunt some mammals on land. This species drowns prey, holding them down with its specially designed teeth for grabbing, not ripping. Preferring to hunt at night, the Black Caiman uses its acute sight and hearing to locate its prey.
The Black Caiman is one of four apex predators in the Rio Negro-Juru Moist Forests, including the Giant Otter, the Green Anaconda and the Jaguar. It is an opportunistic hunter and can metabolically live off of its food for longer than any of the other apex predators in this ecosystem so it hunts more infrequently.
BIODIVERSITY BENEFIT
Population Control
THREATS
Hunting
Heavily hunted for its skin.
Habitat Loss
Deforestation and burning of swamp lands.
Competition
Competition with other caiman species.
PROTECT THE WILDARK 100