Pygmy Hippo
(Choeropsis liberiensis)

Guinean Moist Forests
STATISTICS
Weight up to
275 kgs
Lifespan
40 years
Swimmer - Makes Own Sunscreen
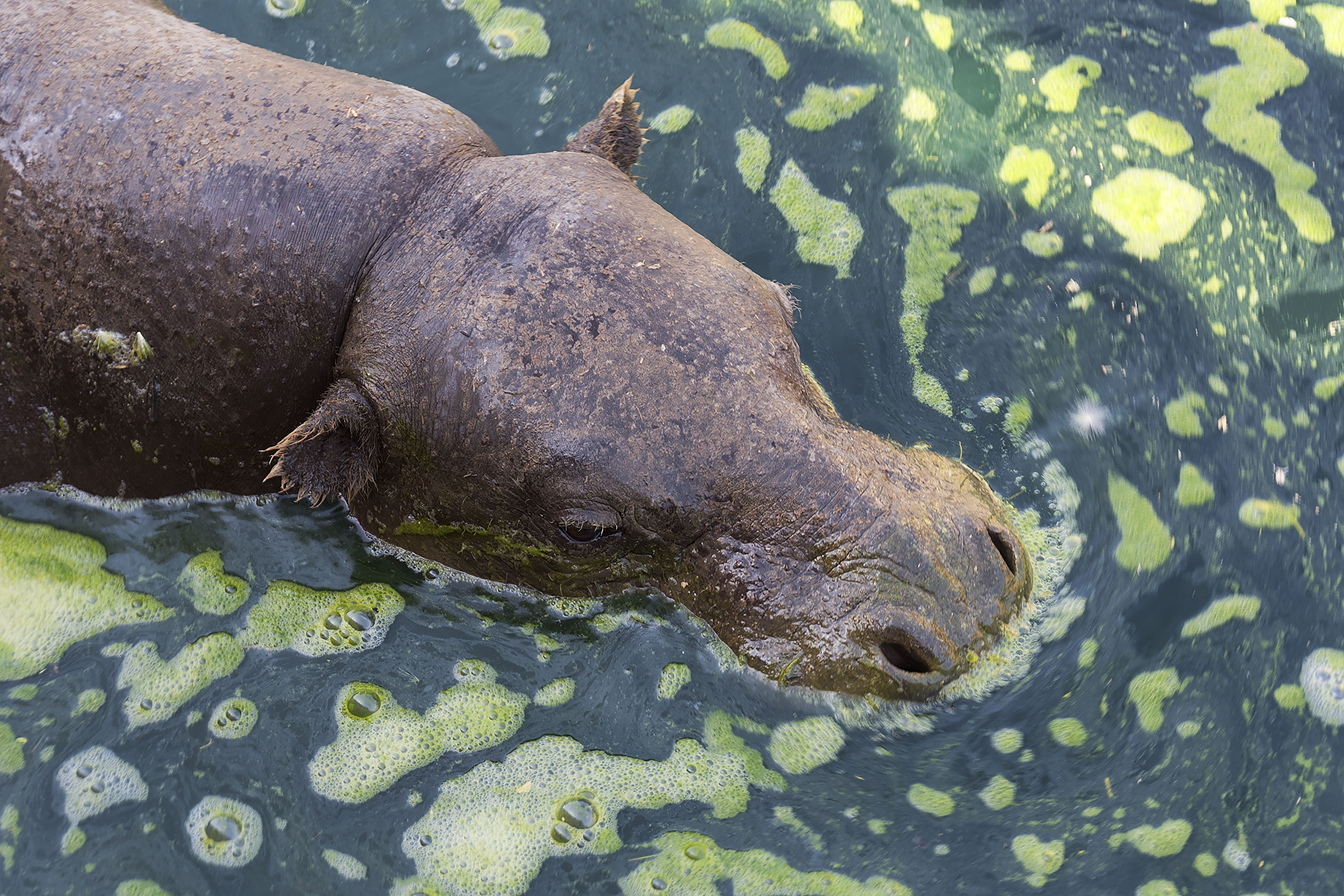
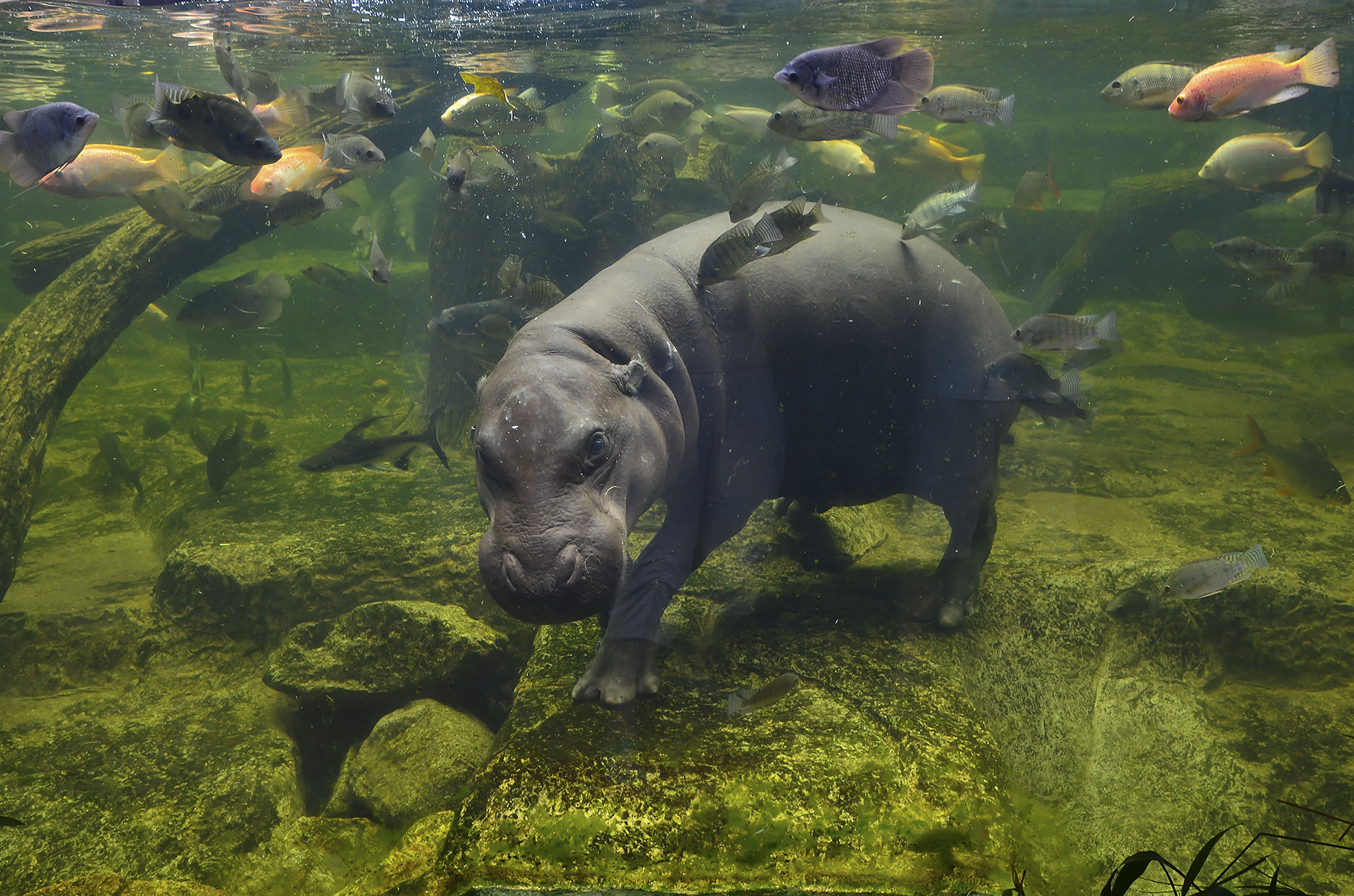
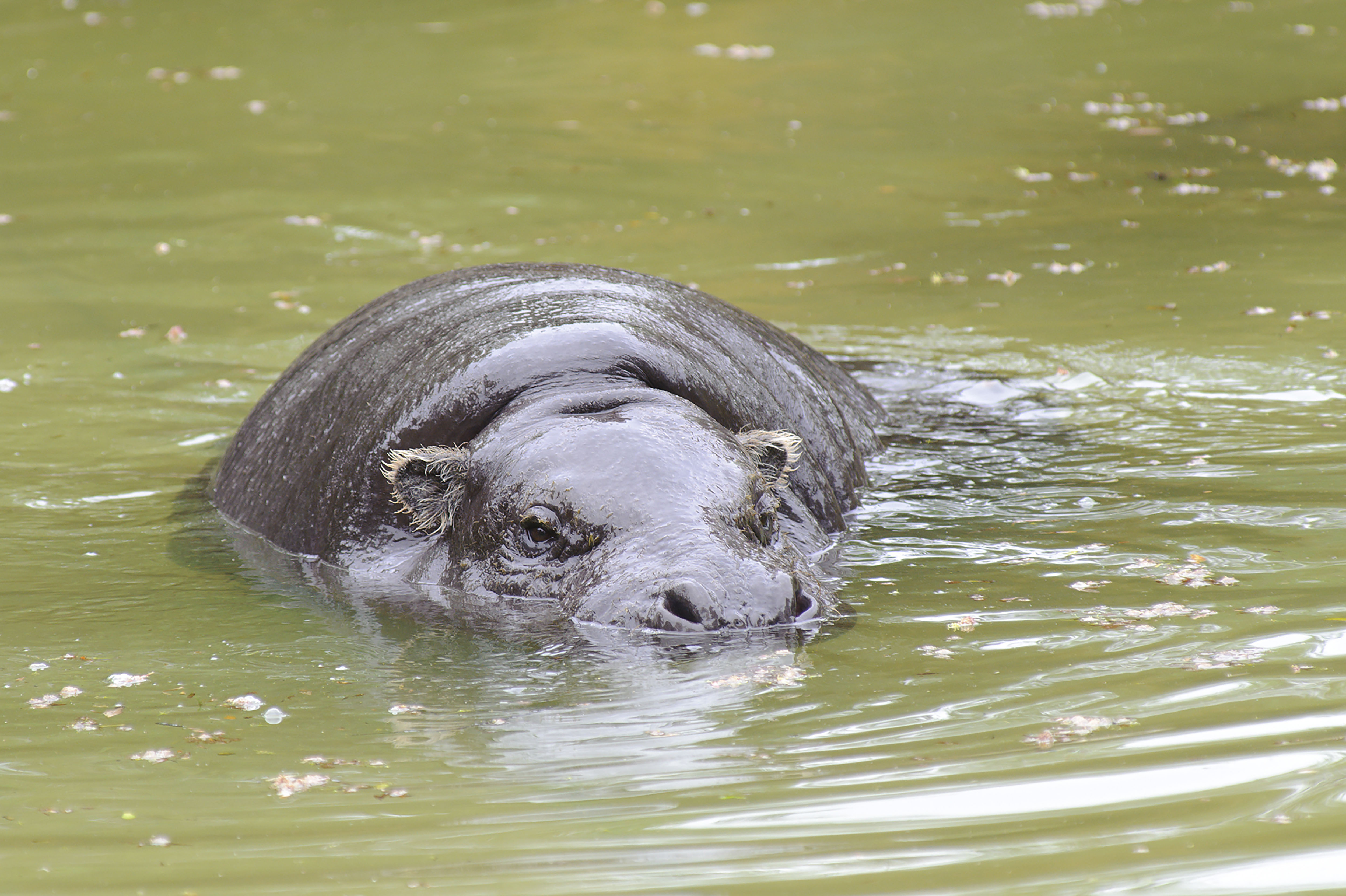
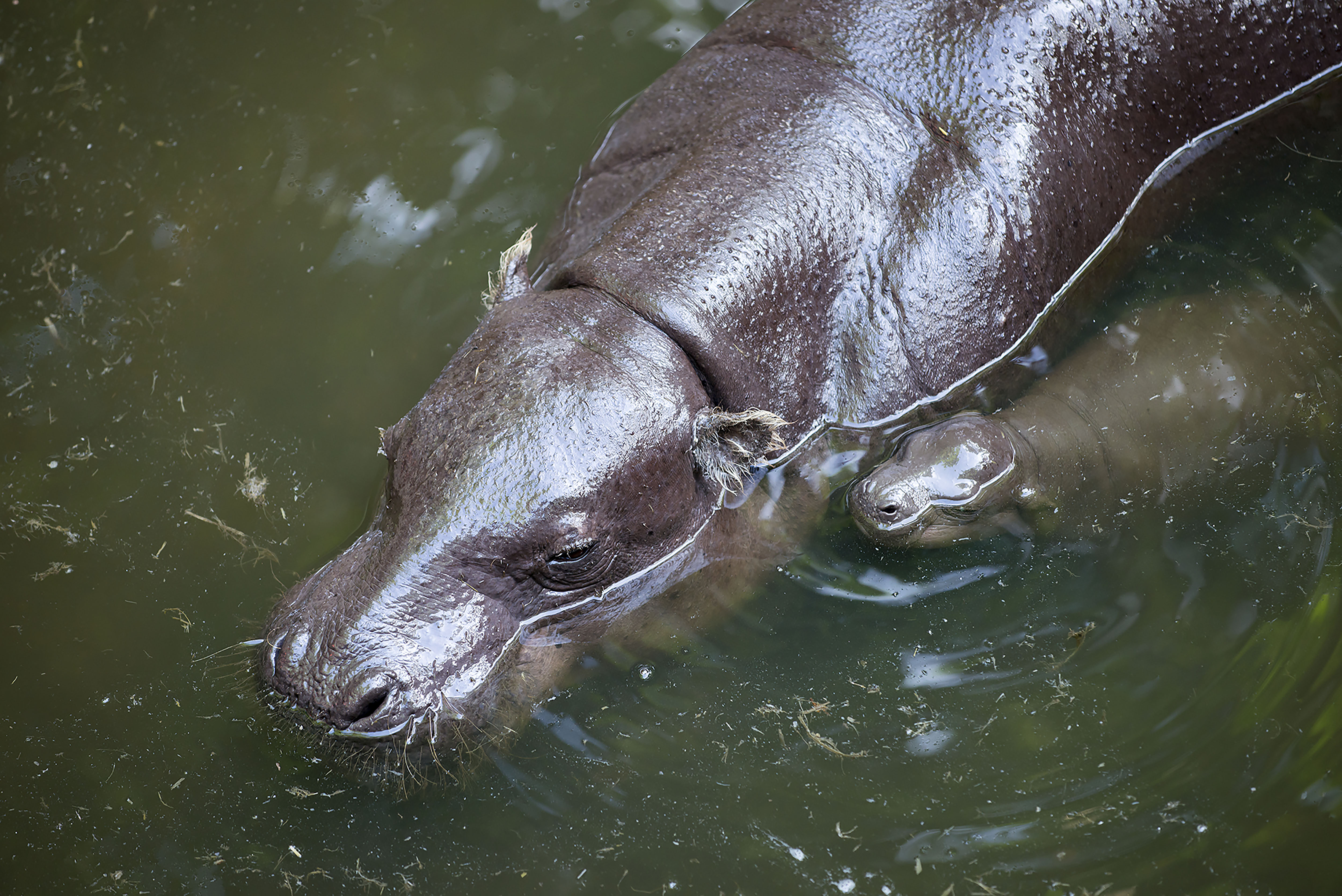
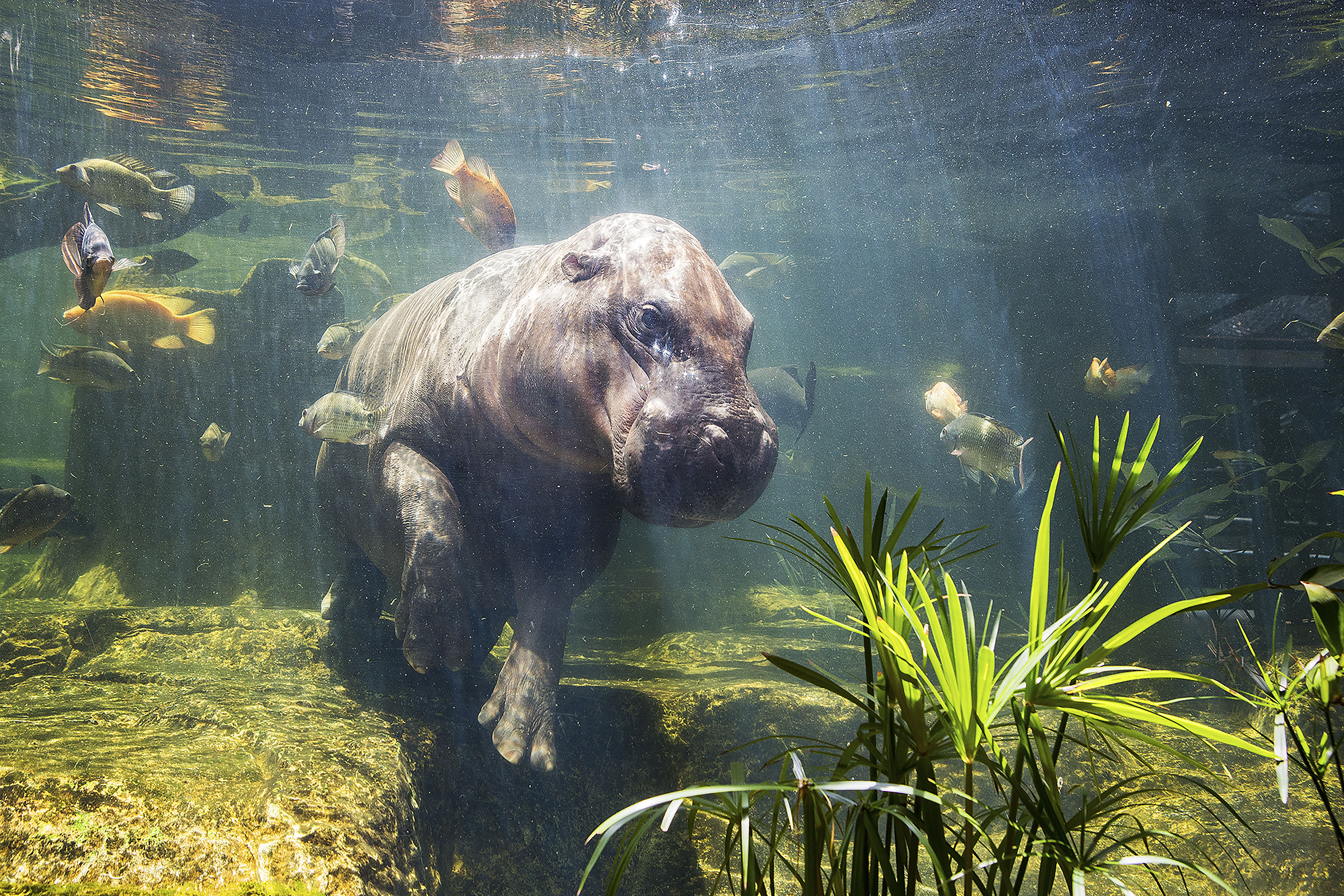
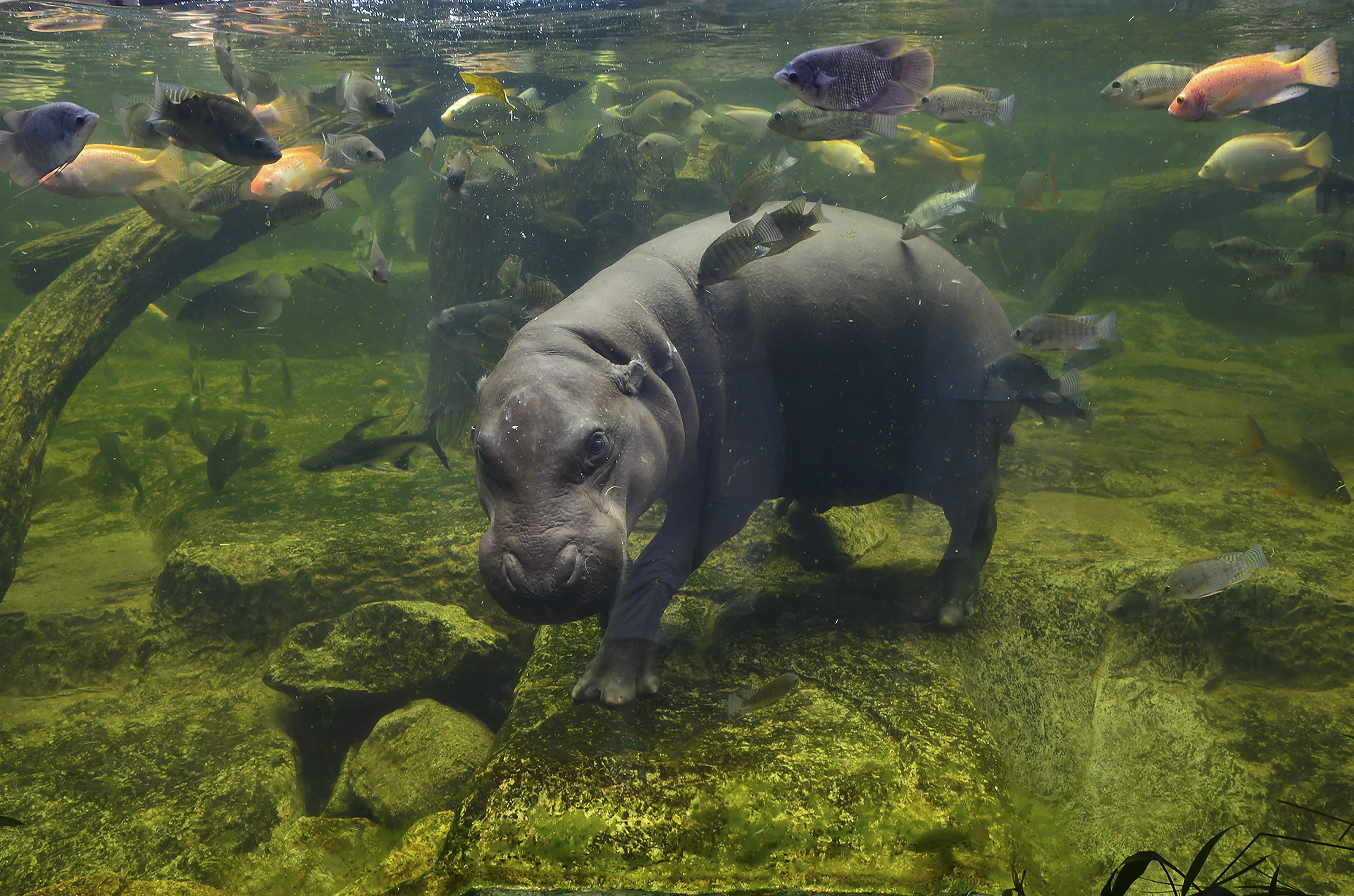
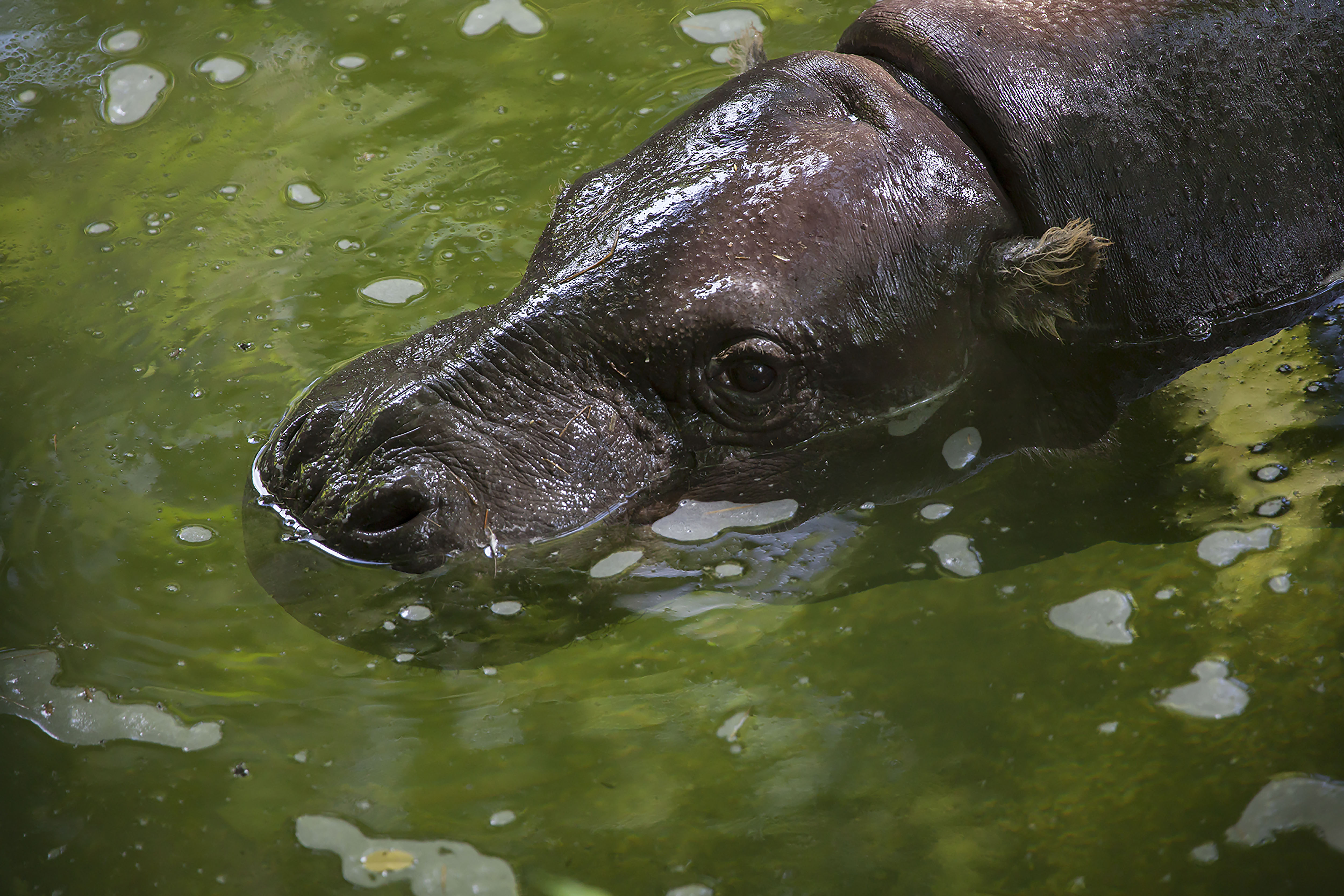
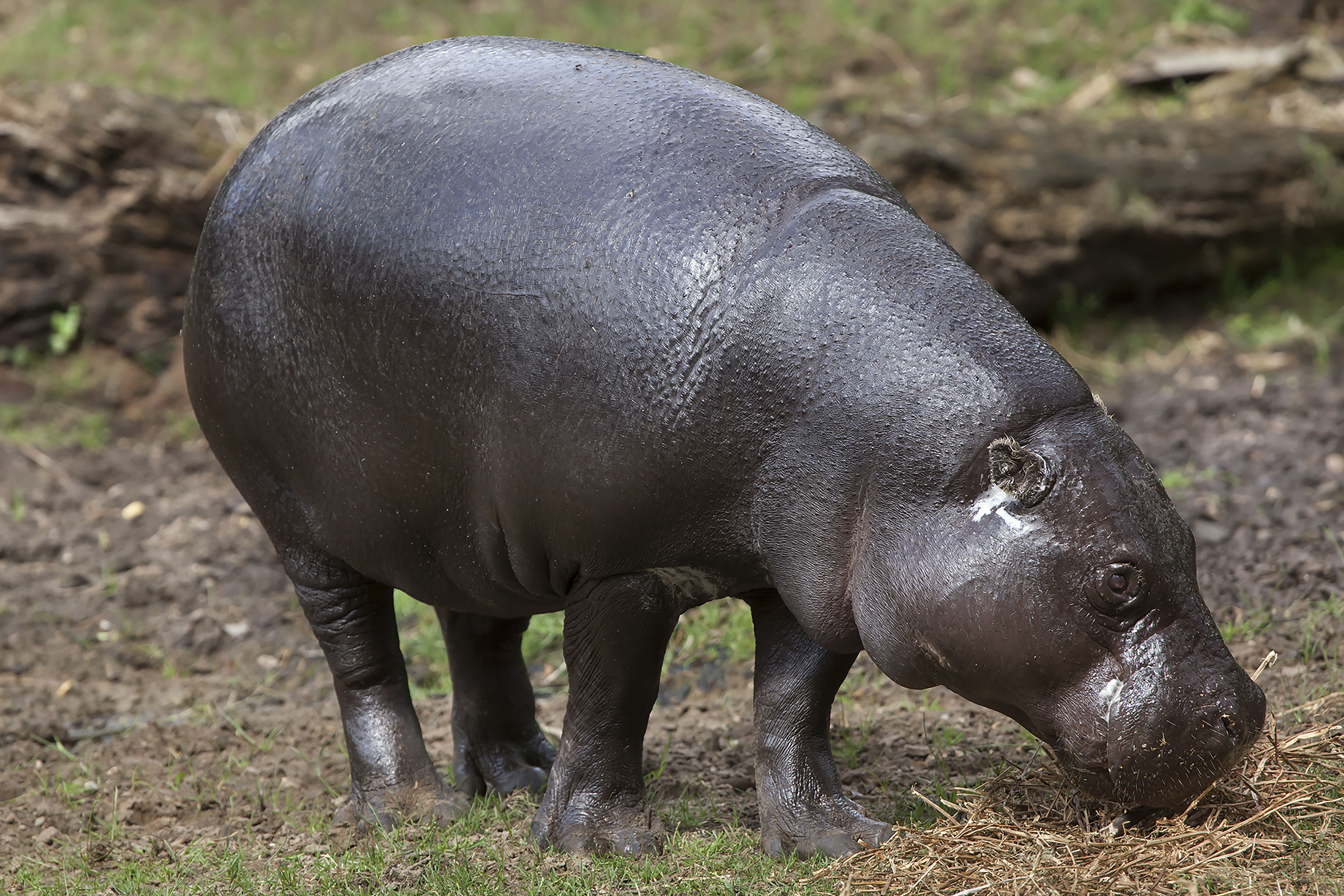
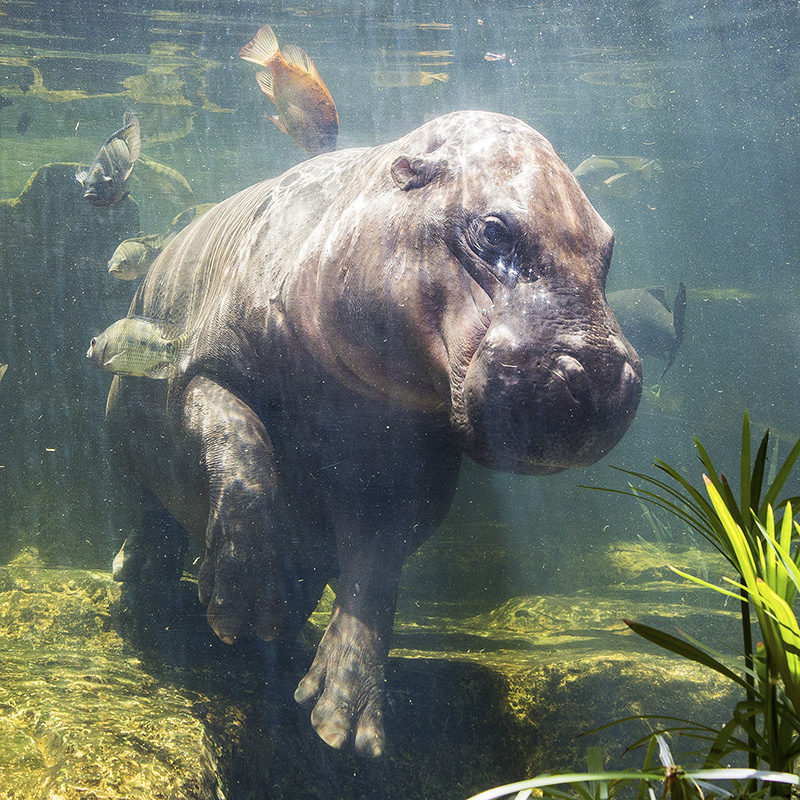
This is a distinct evolutionary species that is about one fifth the size of its cousin, the common Hippopotamus. It resides in low-lying, forested areas, never far from a source of water. It has less webbing between its feet and spends less time in the water than its relative, but it enjoys cooling off in the mud. It is dark brown on top and lighter underneath and has large glands in its skin that produce a glossy secretion, referred to as blood-sweat, that protects its skin from the sun.
The Pygmy Hippo plays an essential role in the ecosystem and uses its feces to mark its presence. It is a solitary species and strictly herbivorous, feeding primarily on plants including grass, herbs, ferns and fruits. Eating on land and excreting in the water, it brings nutrients into the water that wouldn’t otherwise be there. It also creates and changes the landscape around it due to its sheer size, creating channels and paths which, in time, provide shelter for other species. This species’ main predator is the leopard.
BIODIVERSITY BENEFIT
Nutrient Cycling - Habitat Creation
THREATS
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
Forests logged, farmed, or converted to plantations.
Hunting
Fragmented forests have made it very easy for bushmeat hunters.
PROTECT THE WILDARK 100